Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses operate. Among the leading cloud service providers, Amazon Web Services (AWS) stands out for its robust features, scalability, and global infrastructure. For small and medium businesses (SMBs), leveraging AWS can bring efficiency, cost savings, and flexibility. However, migrating to the cloud also introduces security challenges, including the need for IoT security. Ensuring your cloud environment is secure, particularly with IoT devices, is crucial to protect sensitive data, maintain customer trust, and comply with regulations. In this blog, we will explore best practices for AWS cloud security specifically designed for small and medium businesses. These practices will help SMBs maximize the benefits of AWS while minimizing risks.
Summary
AWS cloud security is a shared responsibility, and SMBs must take proactive steps to protect their data and systems. By implementing multi-factor authentication, strong IAM policies, encryption, monitoring, network security, regular updates, backups, ransomware protection, and employee training, businesses can significantly reduce risks. Regular audits and cloud security reviews further strengthen the overall security posture. Following these best practices ensures SMBs can leverage AWS cloud benefits without compromising security, compliance, or customer trust.

Why AWS Security is Important for SMBs
Small and medium businesses are increasingly targeted by cyber threats because they often lack the resources for comprehensive IT security. A data breach can result in financial losses, reputational damage, and regulatory penalties. AWS provides a shared responsibility model, meaning AWS secures the cloud infrastructure, but businesses are responsible for securing their data and applications within the cloud infrastructure during cloud migration. Understanding this shared responsibility model is key to protecting your business from vulnerabilities.
Best Practices for AWS Cloud Security
Here are the essential practices SMBs should implement to ensure AWS security:
1. Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds an extra layer of cloud security by requiring two forms of verification for AWS accounts. Even if a password is compromised, unauthorized access is prevented, which is a critical skill for cloud computing jobs that focus on security.
- Enable MFA for all IAM users.
- Use hardware or virtual MFA devices.
- Consider MFA for root accounts as mandatory.
2. Implement Strong Identity and Access Management (IAM)
AWS IAM is essential for cloud security, as it allows you to manage users, roles, and permissions effectively.
Key practices:
- Use least privilege principle: Give users only the permissions they need.
- Regularly review IAM roles and permissions.
- Avoid using root accounts for daily operations.
- Enable AWS IAM Access Analyzer to detect overly permissive policies.
3. Encrypt Data at Rest and in Transit
Data encryption is a vital part of cloud security, ensuring that even if data is intercepted, it cannot be read without the encryption key.
- Use AWS Key Management Service (KMS) to manage encryption keys.
- Enable encryption for S3 buckets, EBS volumes, and RDS databases.
- Use SSL/TLS to encrypt data in transit between users and AWS services.
4. Monitor and Audit Cloud Activities
Monitoring helps detect unusual activities before they escalate into serious threats.
- Enable AWS CloudTrail to log API calls.
- Use Amazon CloudWatch for monitoring performance and security metrics.
- Set up alerts for suspicious login attempts or configuration changes.
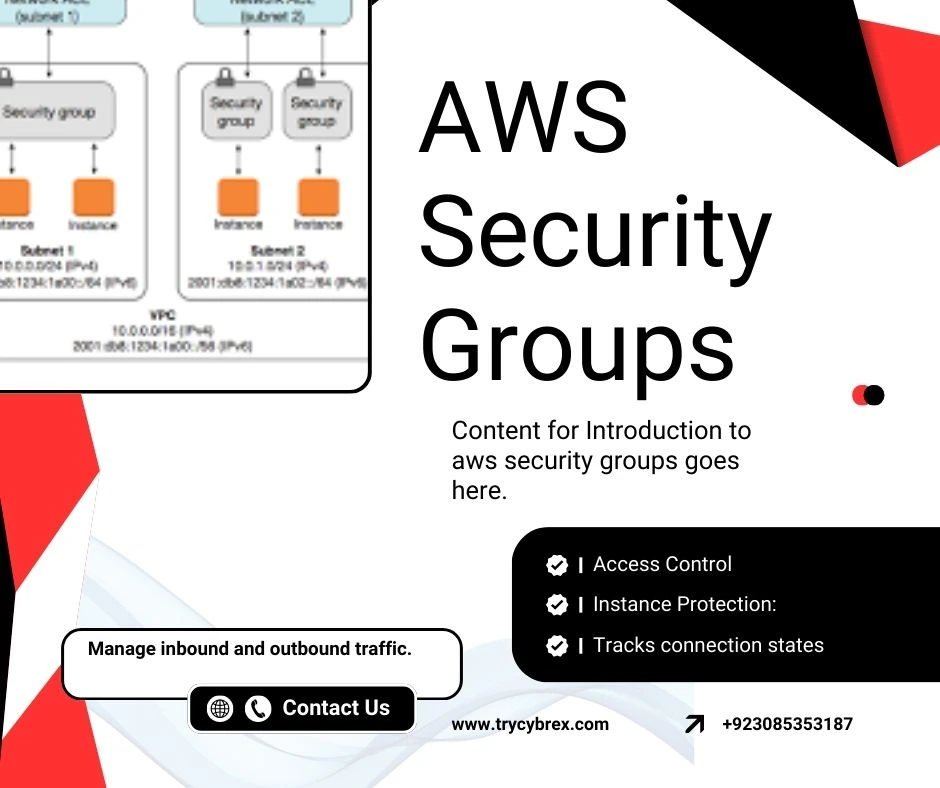
5. Secure Your Network
Proper cloud security and network measures ensure that only authorized users can access your AWS environment.
- Use Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) with subnets for isolating workloads.
- Implement security groups and network ACLs to control traffic.
- Enable AWS WAF (Web Application Firewall) to protect web applications from attacks.
6. Regularly Patch and Update Systems
Unpatched software is a common attack vector.
- Regularly update AWS-managed services.
- Use AWS Systems Manager for automated patching.
- Keep your operating systems and applications up to date.
7. Backup and Disaster Recovery Planning
Data loss can be catastrophic. SMBs must have a recovery plan.
- Use AWS Backup to automate backups.
- Enable versioning in S3 buckets.
- Test disaster recovery strategies regularly.
- 8. Enable Security Best Practices for Applications

Applications hosted on AWS should follow security best practices.
- Conduct code reviews and penetration testing.
- Implement API security with proper authentication and authorization.
- Use AWS Shield to protect against DDoS attacks.
9. Educate and Train Employees
Human error is a leading cause of security breaches.
- Conduct regular security training sessions.
- Teach staff to recognize phishing and social engineering attacks.
- Encourage strong password practices. if you more read relvent post then click this link WordPress Malware Removal 10 Signs Your Site Is Infected & How to Fix It.
10. Regularly Review Security Configurations
SMBs often overlook periodic reviews, which can leave gaps in security.
- Use AWS Trusted Advisor for security checks.
- Review S3 bucket permissions and access logs.
- Conduct internal security audits quarterly.
Conclusion
For small and medium businesses, AWS offers unparalleled opportunities for growth and efficiency. However, cloud adoption must be accompanied by a robust security strategy. By embracing these best practices, SMBs can secure their cloud environment, prevent data breaches, and focus on scaling their business confidently. Remember, cloud security is an ongoing process, not a one-time setup. Consistency, awareness, and proactive measures are the keys to success.